Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 microscale localisation observation
microscale localisation observationDohi, Terumi; Iijima, Kazuki; Machida, Masahiko; Suno, Hiroya*; Omura, Yoshihito*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kimura, Shigeru*; Kanno, Futoshi*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 17(7), p.e0271035_1 - e0271035_21, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.8(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Dohi, Terumi; Omura, Yoshihito*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kanaizuka, Seiichi*; Nakama, Shigeo; Iijima, Kazuki
PLOS ONE (Internet), 16(5), p.e0251828_1 - e0251828_16, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Kiminori*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku
Geophysical Research Letters, 29(8), p.68_1 - 68_3, 2002/05
The in situ viscosity measurements of the pure molten Fe under high pressures were made by falling sphere X-ray radiography method. Viscosity coefficients at about 2000 K were 15-24 mPa s at 2.7-5.0 GPa, and 4-9 mPa s at 5.0-7.0 GPa. Drastic decrease was found at around 5 GPa, at which stable solid phase below the melting temperatures change from delta (bcc) to gamma (fcc) phases. The observation indicates the possibility that the structural change in the molten Fe occurs in a narrow pressure interval (1 GPa) at the similar condition with the phase transformation in the solid.
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku; Maeda, Makoto*; Sato, Jin*; Kubo, Tomoaki*; Kasai, Shizu*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 190(1-2), p.93 - 101, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:68.57(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Fe-FeS melt is thought to be the major candidate of the outer core material. Its viscosity is one of the most important physical properties to study the dynamics of the convection in the outer core. We performed the in situ viscosity measurement of the Fe-FeS melt under high pressure using X-ray radiography falling sphere method with a novel sample assembly. Viscosity was measures in the temperature, pressure, and compositional conditions of 1233-1923 K, 1.5-6.9 GPa, and Fe-Fe 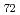 S
S 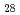 (wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm
(wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm  /mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe
/mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe 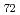 S
S 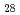 melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.